Engineering Lifecycle Management for Medical Devices
Develop high quality medical devices by leveraging reused concepts, collaboration, traceability, and full compliance to medical standards
As devices become more complex and connected, IBM helps you balance rapid innovation with compliance guidelines and regulations, such as:
- IEC 62304
- FDA Design Controls (21 CFR P. 820.30)
- FDA electronic records & signatures (21 CFR P. 11)
- EU MDR
With IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management, you can manage system requirements, establish tracebility, maintain extreme quality control, classify risks, ensure proper mitigation of hazards, and guarantee quality through rigorous testing. Implement innovative ideas, new functionalities, manage changes, versions and variants and much more thanks to IBM ELM.
Engineering Lifecycle Management for Medical Devices
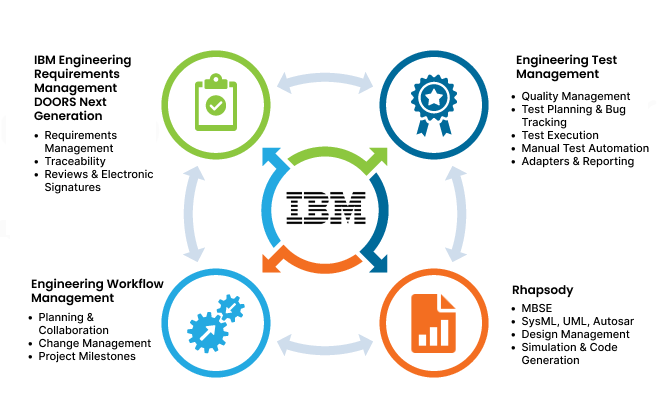
Softacus solutions based on IBM ELM for Medical Devices
Softacus offers a modeling-driven approach for streamlined medical device development.
Our solution ensures:
- Consistency and Traceability: Model-based implementation maintains consistency between device software and documentation, enhancing traceability.
- Development: Facilitates early design validation and testing, promoting repetitive development.
- Submission Documentation Automation: Automates submission document generation, ensuring accuracy and rapid updates when changes occur.
- Quality Management: Establishes a central repository for quality and test assets, reducing the risk of costly recalls.
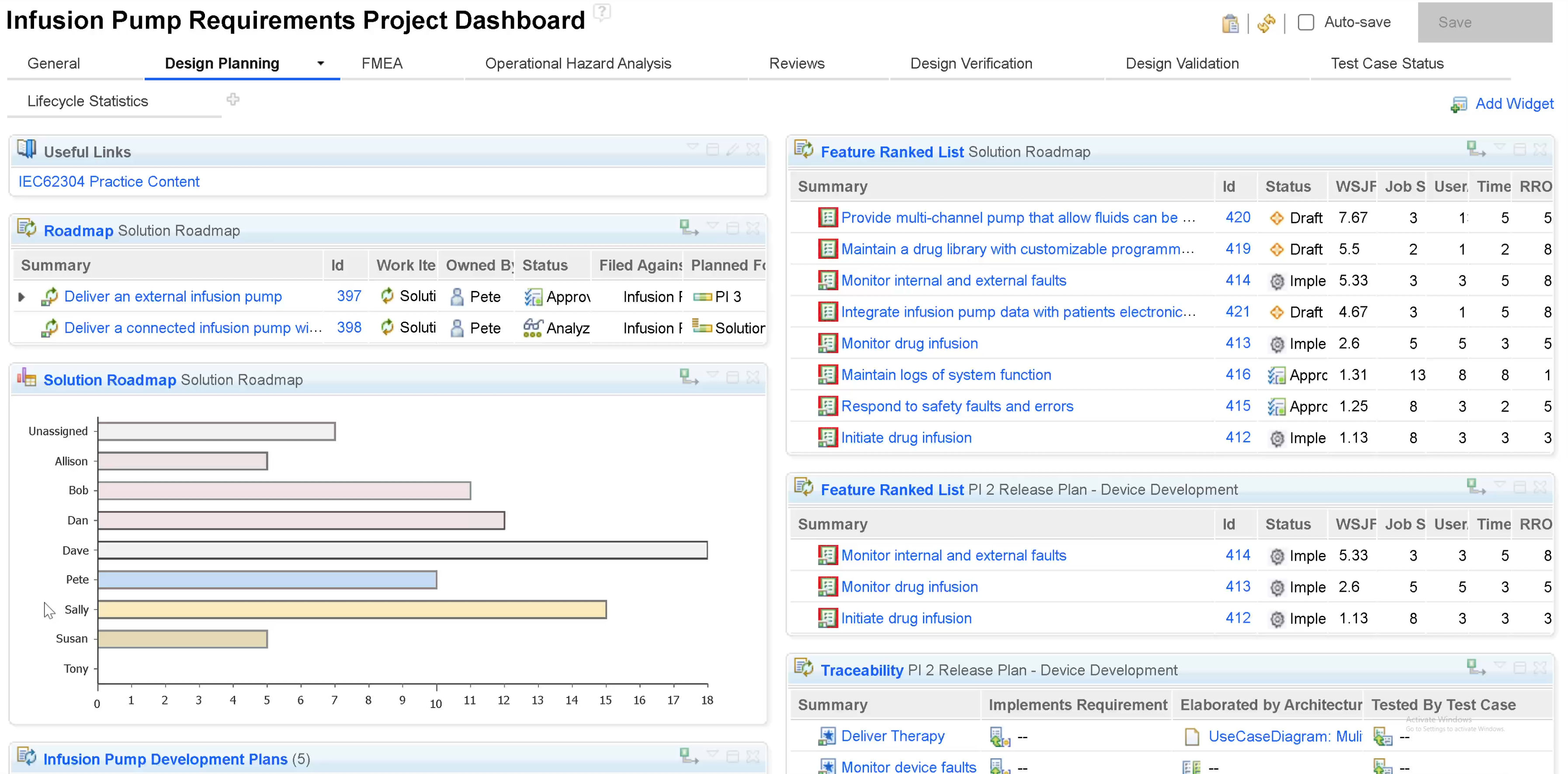
Requirements management
Manage design controls for device requirements.
Define requirements - from vision all the way to engineering details. Include all, inputs, outputs, risks, relationships, dependencies, changes and comprehensive reviews. Maintain design control specifications in a central, automated repository.
In the context of IBM Engineering Lifecycle Management (ELM) for medical devices, a requirements management diagram can play a pivotal role in visualizing and organizing the complex web of requirements that are integral to the development and regulatory compliance of medical devices.
- System Architecture Diagrams: These diagrams provide a high-level overview of the medical device's structure, illustrating how various components interact and work together to fulfill system requirements. They aid in identifying critical interfaces and dependencies within the system, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of its architecture.
- Use Case Diagrams: Use case diagrams help capture the functional aspects of the medical device by showcasing the various user interactions and system responses. These diagrams are instrumental in defining user requirements and validating that the device meets user needs effectively.
- Requirements Traceability Diagrams: Traceability diagrams establish clear connections between system requirements, design elements, and test cases. They help ensure that every requirement is adequately addressed throughout the development lifecycle, contributing to compliance with regulatory standards such as ISO 13485.
- State Diagrams: State diagrams depict the different states a medical device can transition through during its operation. These diagrams are especially valuable in clarifying the behavior of the device under various conditions and guiding the development of accurate and reliable software.
- Flowcharts: Flowcharts provide a visual representation of procedural workflows and decision-making processes within the medical device. They are beneficial for ensuring that the device operates seamlessly and that critical safety protocols are in place.
- Risk Assessment Matrixes: Diagrams such as risk assessment matrixes offer a structured approach to identifying, evaluating, and mitigating risks associated with a medical device. These visual tools enable teams to prioritize risk management strategies effectively.
- Data Flow Diagrams (DFD): DFDs help in understanding how data flows within the system, assisting in the design of data handling processes, which is particularly important in medical devices to ensure data accuracy and patient safety.
- Sequence Diagrams: Sequence diagrams depict the interactions between various components or actors in a chronological order, offering insights into the dynamic behavior of the medical device during specific scenarios.
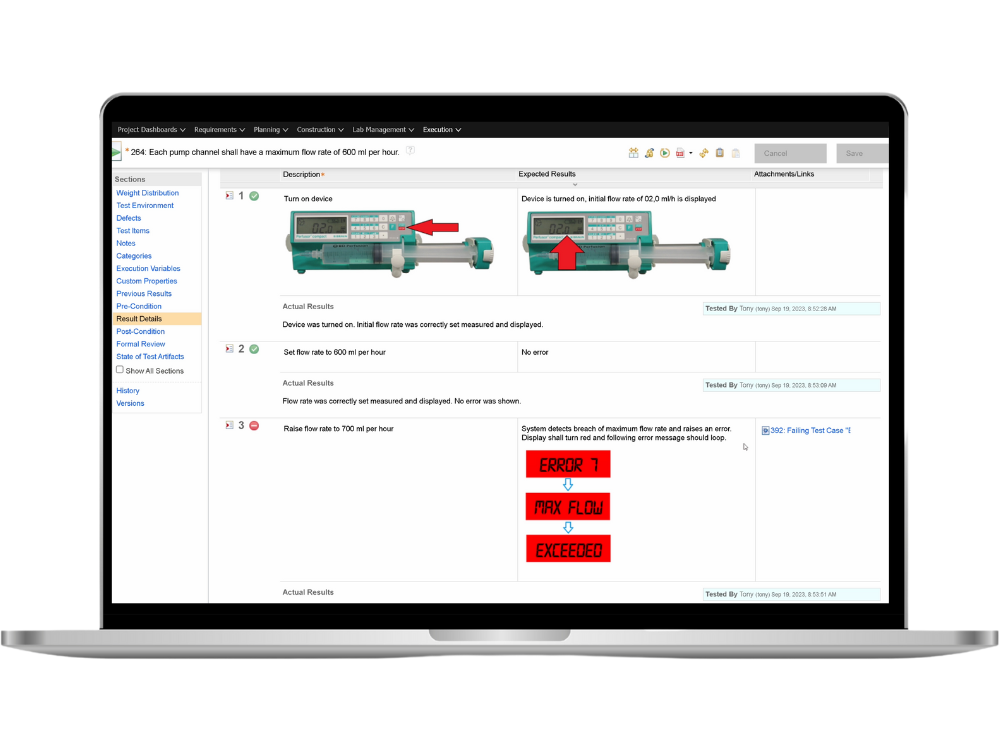
Test Management
Focus on continuous verification and validation.
Plan, review and execute test cases from unit level tests through integration tests all the way up to system tests. Establish TRACEABILITY AND LINK EVERY TEST case with requirements. Meet the requirements of standards like IEC62304, ISO 13485 and 21 CFR P. 820.30
Project management
Manage project and enforce project governance.
Create custom automated workflows, approval processes and use e-signature to sign formal reviews. Identify development tasks, deliverables and link them to requirements as well as to teams, individuals and project roadmap.
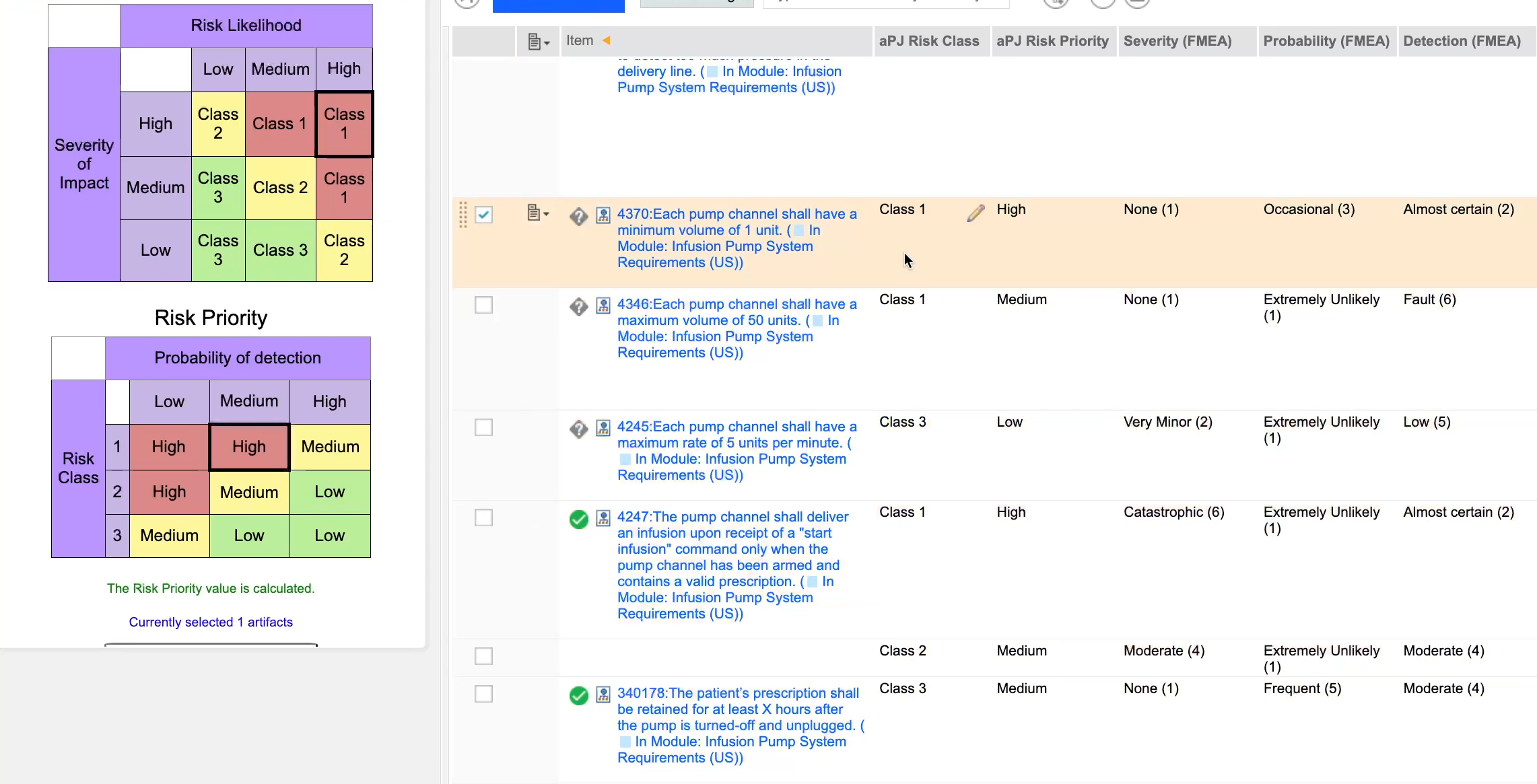
Risk management
Implement risk management process that covers every phase of product lifecycle.
Identify, analyse, calculate, clasify, link, control and mitigate risks to prevent harm or reduce the likelihood of harm occurring, as required by FDA and EU MDR.
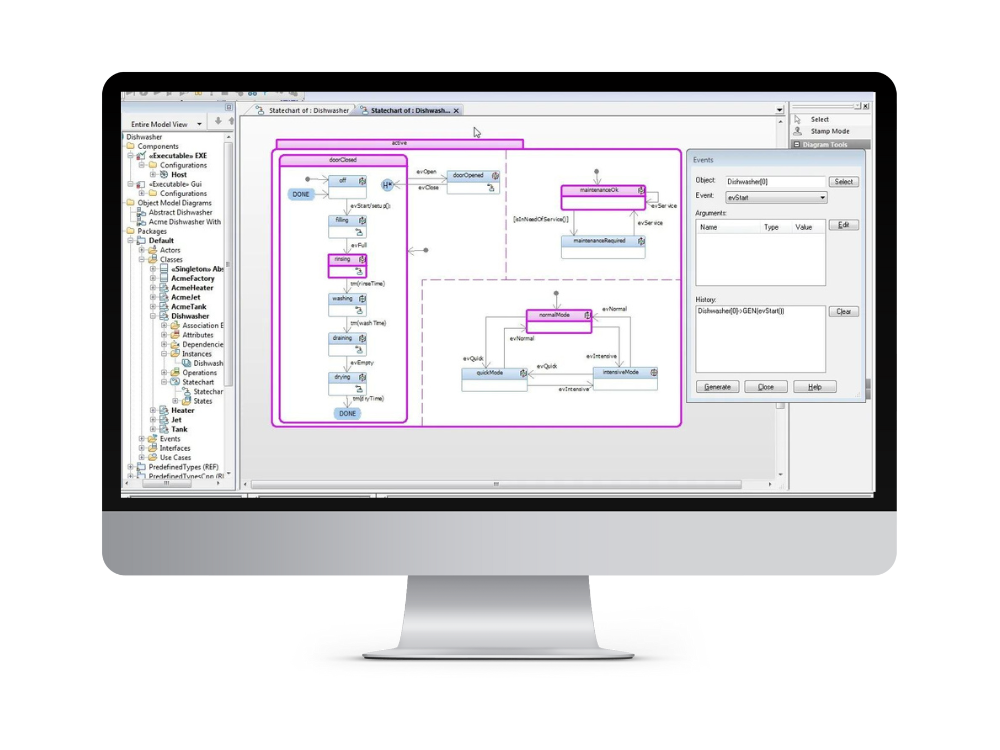
Modeling and simulation
Use model based system and software engineering practices to model, design, build and validate system architecture. Analyze and elaborate requirements through prototypes, simulations and model based testing.
Create, manage and execute SysML and UML models.
Documentation and Compliance
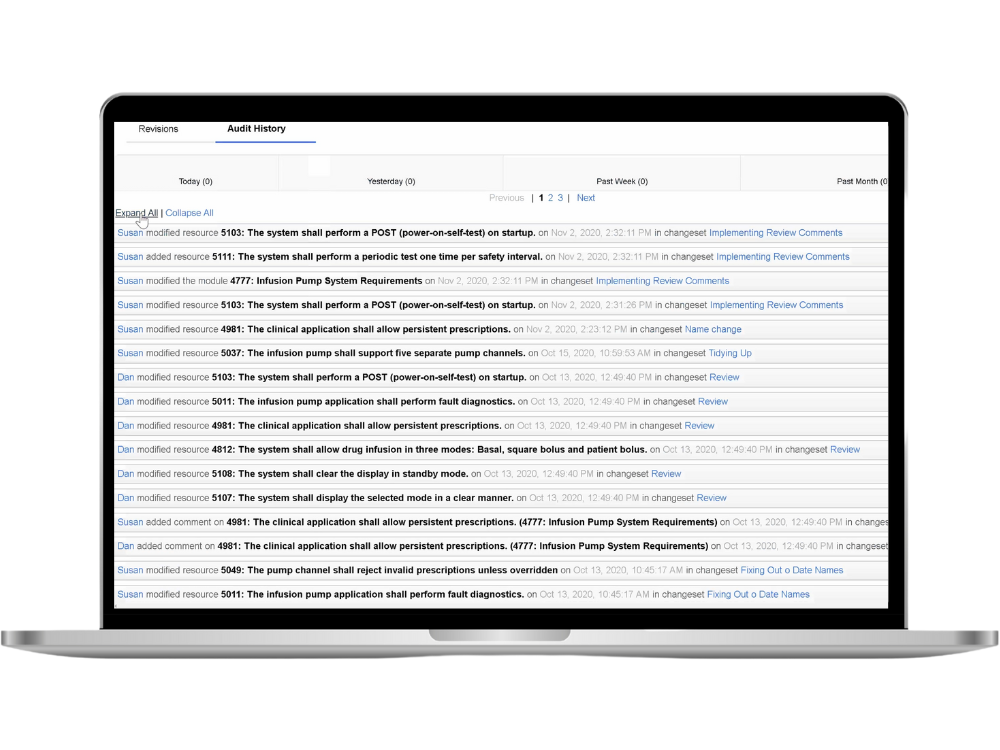
Capture and track every change throughout design history.
Manage compliance by automated capture and creation of up to date design history files, complete traceability report that links the entire process cycle, comprehensive documentation and clinical evaluation reports as required by FDA and EU MDR.
Medical Device Solutions Built on IBM ELM
Success stories of our clients
Whitepapers
Overview of the solution for medical devices and its added value for development teams. Softacus Flyer
Improving development processes using IBM Rational DOORS Requirements Management software in Medical Devices Industry
Accelerate development of products while meeting IEC 61508, IEC 62304, ISO 14971, ISO 13485 and 21 CFR 820.30
Address the FDA identified lack of design controls as one of the major causes of device recalls
How to manage your compliance with IBM Tools in Medical Device Development
Automating product development and compliance processes using IBM Rational software
This paper will explore what IEC 62304 compliance means for manufacturers in some detail, and also describe the larger context of systems and software engineering best practices at work in many of today’s most successful companies.
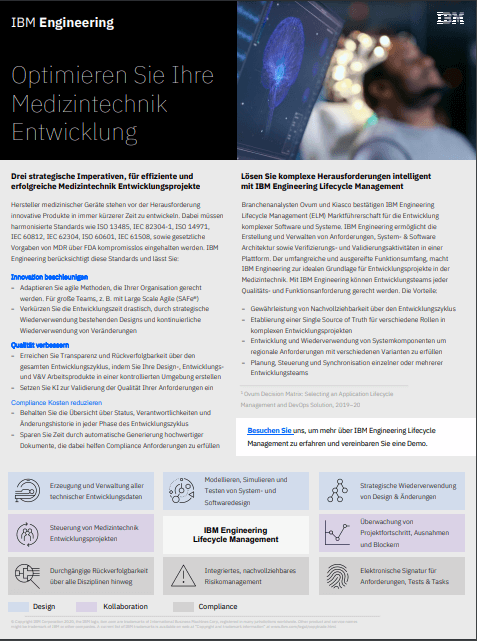
Drei strategische Imperativen, für effiziente und erfolgreiche Medizintechnik Entwicklungsprojekte
Improve processes, manage IEC 61508 and IEC 62304 standards, develop quality products
Industry leaders are using IBM ELM solutions

Aerospace & Defense Companies

Automotive Manufacturers

Smart Phone Manufacturers

Medical Device Manufacturers

Pharmaceutical Companies

Semiconductor Companies
Contact Us
More about
IBM ELM supports companies developing medical devices to comply with the ISO 14971.
Read MoreLearn how IBM ELM helps you achieve compliance with the international standard IEC 62304 to satisfy all your workflow needs.
Read MoreFailure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a structured approach to discovering potential failures that may exist within the design of a product or process.
Read More